GBS Testing

Group B Stretptococcus (GBS)
Patient Information Sheet


Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a type of normal bacteria that is commonly found in the birth canal (10-30% of pregnant women). A women with GBS can pass it to her baby during labour & birth. Most babies who are exposed to this GBS bacteria during labour do NOT become sick.
A few however, will become very ill. If a woman has GBS, treatment with antibiotics during labour may help prevent infection in her baby. This is why it is strongly suggested, that all pregnant women be tested for GBS bacteria between 35-37 weeks of pregnancy.
A woman may taker her own vaginal and rectal swab by following these instructions. We suggest that you do this on the morning of your regular prenatal visit at 35 or 36 weeks.
If you have any questions please let us know.
1. Open the top of the package by peeling apart the plastic wrap.
2. Twist off the white top of the container and throw the top away.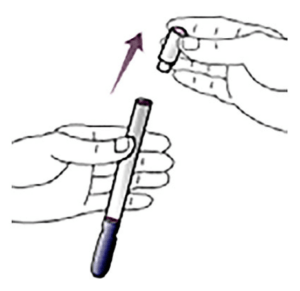
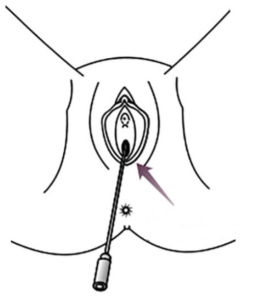
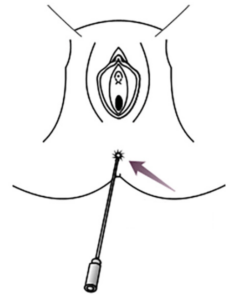
4. Put the swab about 2 cm (1 inch) into the opening of your vagina and gently twist.
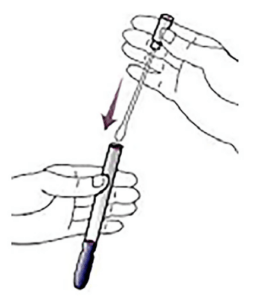
See this useful video
How do I know if I have GBS?
As GBS is a normal bacteria there are no symptoms. You will require a swab in order to know you have GBS. Sometimes it is detected in a urine sample.
Who needs treatment for GBS?
Antibiotics for GBS will be given in the following situations:
- Your GBS swab was positive and you are in labour
- Your GBS swab was positive and your have broken
- You have tested positive for GBS in Urine and are in labour or your waters have broken
- You are in labour before 37 weeks and your GBS swab is not back yet.
- You have had a previous baby with a GBS infection
What is the treatment for GBS?
Treatment for GBS is usually with Penicillin or Ampicillin. It takes 4 hours for treatment to be considered adequate. While antibiotics reduce the risk of infection, they do not eliminate the risk completely.
If you have an allergy to Penicillin, please share this with your obstetrician.
If I test Positive for GBS should I get treatment immediately?
This is a very common question. Because GBS is a normal bacteria, it is likely to return after treatment.
As such treatment for GBS is started:
- during active labour
- you have broken your waters before labour
What happens if I do not test for GBS?
If you have GBS and it is not treated during labour, there is a small risk of your baby developing a serious infection.
Will I have GBS forever?
In many patients, GBS will come and go over time.
How reliable is the test?
Screening is very good, but not perfect. The swab test may not detect approximately 1 in 20 women who are in fact positive for GBS.
What happens if I break my waters before labour?
If you break your waters before labour has begun, please come to the hospital. Your doctor will recommend starting treatment for GBS and induction to start the labour. (Shortening the time to delivery will also reduce the risk of your baby getting an infection.)
What if I am having a c-section?
Patients who have a planned c-section doe not require GBS treatment. However, sometimes patients who are planning a c-section end up having an unplanned vaginal delivery, so GBS swabs are recommended for all patients.
How long do results take?
Additional Resources
- Click here to learn more from the SOGC.
- This handout has additional information.




